
A Frame represents a spacial position.
This is typically an object or a person position.
The location of a Frame can be updated after creation, but this will be done differently for
FreeFrame and AttachedFrame:
AttachedFrame is bound to a parent frame, whereasFreeFrame location can be updated freely.For further details, see:
From any existing Frame, it is possible to build a new AttachedFrame,
that moves with its parent frame.
After creation, the offset transform between the parent and the attached frame
can be updated at any time.
This is typically used to define targets for GoTo or LookAt actions relatively to existing frames.
val baseFrame: Frame = ...
val transform1: Transform = TransformBuilder.create().fromXTranslation(1.0)
val attachedFrame: AttachedFrame = baseFrame.makeAttachedFrame(transform1)
val transform2: Transform = TransformBuilder.create().fromXTranslation(2.0)
attachedFrame.update(transform2)
Frame baseFrame = ...;
Transform transform1 = TransformBuilder.create().fromXTranslation(1);
AttachedFrame attachedFrame = baseFrame.makeAttachedFrame(transform1);
Transform transform2 = TransformBuilder.create().fromXTranslation(2);
attachedFrame.update(transform2);
A FreeFrame represents a location free to be placed anywhere, that
does not move when other frames move.
It is created from the Mapping service.
The global position of a free frame can be updated by giving its
Transform in another frame at any time, see Timestamps.
Free frames are typically used by services detecting objects or persons in the
environment, and updating periodically their location relatively to the robot.
When the transform between a base frame and the updated free frame comes from
robot sensor data, it is recommended to use the timestamp associated with that
data when updating the free frame. If no timestamp is available,
FreeFrame.update() can be called with an arbitrary 0 timestamp. The method
will fall back on updating the free frame relatively to the last known location
of the base frame.
val mapping = qiContext.mapping
val freeFrame: FreeFrame = mapping.makeFreeFrame()
val baseFrame: Frame = ...
val transform: Transform = ...
freeFrame.update(baseFrame, transform, timestamp)
Mapping mapping = qiContext.getMapping();
FreeFrame freeFrame = mapping.makeFreeFrame();
Frame baseFrame = ...;
Transform transform = ...;
freeFrame.update(baseFrame, transform, timestamp);
You can use a Frame to specify a location where Pepper should go to:
val targetFrame: Frame = ...
val goTo: GoTo = GoToBuilder.with(qiContext)
.withFrame(targetFrame)
.build()
goTo.async().run()
Frame targetFrame = ...;
GoTo goTo = GoToBuilder.with(qiContext)
.withFrame(targetFrame)
.build();
goTo.async().run();
You can also use a Frame to specify a location where Pepper should look at:
val targetFrame: Frame = ...
val lookAt: LookAt = LookAtBuilder.with(qiContext)
.withFrame(targetFrame)
.build()
val lookAtFuture: Future<Void>? = lookAt?.async()?.run()
Frame targetFrame = ...;
LookAt lookAt = LookAtBuilder.with(qiContext)
.withFrame(targetFrame)
.build();
Future<Void> lookAtFuture = lookAt.async().run();
Frame representing the robot location.
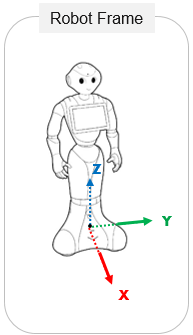
It can be retrieved using the Actuation service:
val actuation: Actuation = qiContext.actuation
val robotFrame: Frame = actuation.robotFrame()
Actuation actuation = qiContext.getActuation();
Frame robotFrame = actuation.robotFrame();
Frame representing the human location.
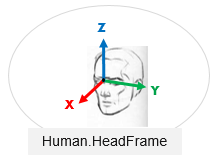
It is accessible via a Human instance:
val human: Human = ...
val headFrame: Frame = human.headFrame
Human human = ...;
Frame headFrame = human.getHeadFrame();
Frame representing the position and orientation of the robot gaze. When looking at a target, the robot will align this frame x-axis with the target origin.
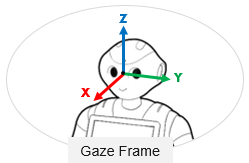
To retrieve it, use the Actuation service:
val actuation: Actuation = qiContext.actuation
val gazeFrame: Frame = actuation.gazeFrame()
Actuation actuation = qiContext.getActuation();
Frame gazeFrame = actuation.gazeFrame();
Frame representing the origin of the map in which Pepper is localized. The Map Frame is not available if the localization process is not running.
To retrieve it, use the Mapping service:
val mapping: Mapping = qiContext.mapping
val mapFrame: Frame = mapping.mapFrame()
Mapping mapping = qiContext.getMapping();
Frame mapFrame = mapping.mapFrame();
Frame representing the position and orientation of Pepper’s charging station. The Charging Station Frame is not available if Pepper has never seen or sensed his Charging Station.
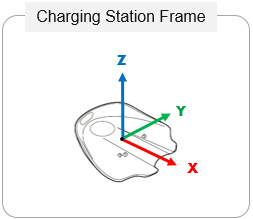
It can be retrieved using the Mapping service:
val mapping: Mapping = qiContext.mapping()
val chargingStationFrame: Frame = mapping.chargingStationFrame()
Mapping mapping = qiContext.getMapping();
Frame chargingStationFrame = mapping.chargingStationFrame();